The Potential Barrier Definition refers to a vicinity inside a fabric or gadget where the capability power creates an obstacle that stops the loose drift of charge carriers, which include electrons. This concept is particularly essential in semiconductor physics, wherein it explains how devices like diodes and transistors work. In a semiconductor, a capability barrier bureaucracy on the junction among distinctive materials, like the p-type and n-kind regions. The fee carriers need sufficient power, which include thermal power or an applied voltage, to triumph over this barrier and permit present day to glide. The Potential Barrier Definition enables in know-how how modern is managed and how electronic components function in gadgets like transistors, diodes, and even in quantum tunneling phenomena.
- What is a Potential Barrier Definition?
- How Does a Potential Barrier Relate to Electrons?
- Role of Potential Barrier in Quantum Mechanics
- Classical vs. Quantum View of Potential Barriers
- Examples of Potential Barriers in Physics
- How Potential Barriers Affect Particle Motion
- Applications of Potential Barriers in Technology
- FAQ About Potential Barrier Definition
What is a Potential Barrier Definition?
A Potential Barrier Definition refers to a region within a cloth or a device where there’s a distinction in the capacity electricity, appearing as a barrier that stops the movement of fee providers, consisting of electrons, from one area to every other. This phenomenon is especially vital in the observe of semiconductors and is key to the functioning of many electronic gadgets, which includes diodes and transistors. A potential barrier normally forms at the junction between distinctive materials or areas with wonderful electricity degrees, like the p-type and n-type areas in semiconductors. Charge carriers need to overcome this power barrier to allow modern to glide.
Key Points:
- Formation: A potential barrier paperwork while there is a discontinuity inside the power ranges of different materials or regions, which include in semiconductor junctions.
- Role in Semiconductors: In semiconductor gadgets, the potential barrier is critical for controlling the drift of modern-day. It bureaucracy at junctions just like the p-n junction in diodes.
- Energy Threshold: Charge vendors need to have enough electricity to triumph over the capacity barrier and flow from one location to another.
- Current Control: The ability barrier facilitates in controlling the course and importance of current in gadgets together with diodes, transistors, and different semiconductor-based totally devices.
- Tunneling: At very small scales, quantum mechanical tunneling can allow fee vendors to bypass via a capacity barrier even if they don’t have enough strength to triumph over it.
How Does a Potential Barrier Relate to Electrons?
- Electrons and Energy Levels: In a fabric, electrons flow based at the electricity ranges to be had to them. The Potential Barrier Definition explains how electrons encounter a region where their electricity is insufficient to conquer a difference in capacity, stopping their motion.
- Electron Confinement: When an electron methods a potential barrier, if its energy is decrease than the power required to surmount the barrier, it will likely be restrained to one facet of the barrier. The Potential Barrier explains this restriction of electron waft.
- Tunneling Phenomenon: In quantum mechanics, if the electron’s power is less than the capacity barrier, it could once in a while nonetheless skip through the barrier due to quantum tunneling, that is a phenomenon defined by using the Potential Barrier Definition.
- Current Flow Control: Electrons can not flow throughout a potential barrier until they’ve enough power to overcome it. The Potential Barrier Definition allows in information how this behavior regulates current in gadgets like diodes and transistors.
- Formation in Semiconductors: In semiconductors, while p-kind and n-type materials are joined, a capability barrier is formed on the junction. Electrons inside the n-type place face this potential barrier while looking to circulate to the p-type location, as defined by way of the Potential Barrier.
- Thermal Excitation: Electrons may additionally benefit sufficient power to overcome the potential barrier through thermal excitation. The Potential Barrier enables in understanding how temperature can provide electrons the desired electricity to move beyond the barrier.
Role of Potential Barrier in Quantum Mechanics
- Quantum Tunneling: The “Potential Barrier Definition” is essential in quantum mechanics, because it allows the phenomenon of quantum tunneling, wherein debris pass thru barriers despite inadequate electricity.
- Wave-Particle Duality: According to the “Potential Barrier,” the conduct of particles is advocated through way of their wave-like houses, inflicting tunneling and distinct quantum consequences.
- Reflection and Transmission: When debris stumble upon a capability barrier, part of the wave is contemplated and component transmitted, primarily based completely on the “Potential Barrier Definition.”
- Energy Quantization: The “Potential Barrier Definition” facilitates decide the discrete electricity ranges that particles can occupy in limited structures like quantum wells.
- Schrödinger’s Equation: The “Potential Barrier” is included into Schrödinger’s equation, affecting how debris interact with the barrier.
- Probability of Tunneling: The danger of a particle tunneling via a barrier is at once precipitated via the “Potential Barrier.”
- Confinement in Quantum Systems: The “Potential Barrier Definition” helps confine particles indoors ability wells, critical in nanotechnology and quantum computing.
Classical vs. Quantum View of Potential Barriers
| Aspect | Classical View | Quantum View |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Behavior | Particles cannot pass through a barrier if their energy is less than the barrier height. | Particles have a non-zero probability of tunneling through a barrier, even with insufficient energy. |
| Energy Threshold | If the particle’s energy is less than the barrier, it is reflected. | Quantum mechanics allows the particle to pass through a barrier, even if its energy is lower than the barrier height. |
| Motion | Particles behave as deterministic objects with clear trajectories. | Particles exhibit wave-like behavior, leading to the phenomenon of quantum tunneling. |
| Barrier Penetration | No penetration of the barrier is possible if energy is insufficient. | There is a finite probability of penetrating the barrier, even when energy is insufficient. |
| Probability | 100% reflection if energy is less than the barrier height. | The probability of tunneling depends on barrier width, height, and particle energy. |
| Wave Function | Not considered in classical physics. | The wave function describes the probability of finding a particle inside or outside the barrier. |
| Role of Uncertainty | Uncertainty does not play a role in classical physics. | Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle governs particle behavior near barriers. |
| Outcome | The particle is either reflected or transmitted based on energy. | The particle has a probability distribution that allows for reflection or transmission. |
| Energy Conservation | Particles must have energy greater than or equal to the barrier to overcome it. | Energy conservation is still upheld, but tunneling can occur, allowing particles to “pass” through barriers. |
| Nature of the Barrier | A well-defined, rigid barrier that particles cannot pass if energy is insufficient. | The barrier is not rigid; it allows for wave-like penetration, albeit with a decreasing probability. |
Examples of Potential Barriers in Physics
- Tunneling in Semiconductor Devices: In devices like tunnel diodes, the capacity barrier among substances lets in for quantum tunneling, permitting present day to waft even though classical theory shows otherwise.
- Energy Barriers in Chemical Reactions: In chemistry, capability obstacles (activation energy) are wanted to break bonds and initiate reactions. In quantum mechanics, tunneling can help particles overcome these barriers at decrease energies.
- Barrier in Nuclear Fusion: In nuclear fusion reactions, the Coulomb barrier prevents nuclei from coming near sufficient to fuse. However, quantum tunneling lets in fusion to occur at decrease temperatures than classical physics predicts.
- Quantum Wells in Nanotechnology: In quantum wells, potential obstacles confine electrons or other particles in a selected region. These obstacles manipulate the digital homes of materials at the nanoscale.
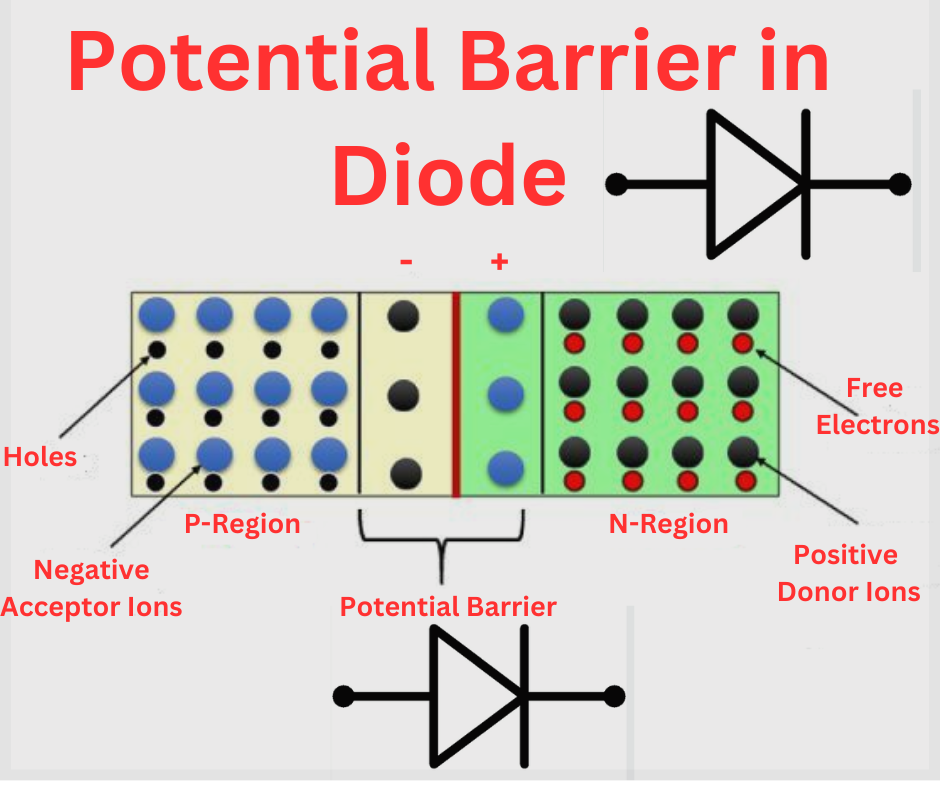
- Potential Barrier in a Diode: In semiconductor physics, the ability barrier at a pn-junction diode prevents the flow of current in one course. Quantum tunneling can nevertheless permit cutting-edge to pass below sure conditions (as in Zener diodes).
- Gravitational Potential Barriers: In astrophysics, a black hollow’s event horizon represents a ability barrier. It prevents something, along with mild, from escaping once it crosses the threshold.
- Magnetic Barriers in Superconductivity: In the phenomenon of the Meissner impact, superconductors create a magnetic ability barrier that excludes magnetic fields from their interior, keeping 0 electric resistance.
How Potential Barriers Affect Particle Motion
- Reflection: Particles with strength less than the barrier are contemplated, as in keeping with the “Potential Barrier”.
- Quantum Tunneling: Even with lower strength, particles can skip via obstacles due to quantum tunneling, explained by means of the “Potential Barrier Definition”.
- Wave Function Decay: Inside a capability barrier, a particle’s wave characteristic decays exponentially, as indicated with the aid of the “Potential Barrier”.
- Transmission Probability: The better and thicker the barrier, the decrease the danger of tunneling, according to the “Potential Barrier Definition”.
- Particle Trajectory: The particle’s route is altered through the potential barrier, with mirrored image or tunneling determined via the “Potential Barrier”.
- Energy Restriction: Barriers save you debris with inadequate energy from passing, in step with the “Potential Barrier”.
- Quantized Energy States: In constrained regions, potential barriers cause discrete strength tiers for debris, as in line with the “Potential Barrier”.
- Electron Flow Control: In semiconductors, the “Potential Barrier” regulates electron waft, permitting or blocking off contemporary based on barrier homes.
Applications of Potential Barriers in Technology
- Semiconductor Devices: Potential limitations are important in the operation of semiconductor additives like diodes, transistors, and tunnel diodes. These barriers alter electron glide, allowing devices like computer systems, smartphones, and solar cells.
- Quantum Tunneling in Tunnel Diodes: In tunnel diodes, ability limitations permit quantum tunneling, main to precise electrical residences. This software is utilized in excessive-speed and occasional-power gadgets.
- Field Emission Devices: Potential obstacles are utilized in field emission displays (FEDs), where electrons tunnel thru a capability barrier to produce light, allowing packages in display technology.
- Quantum Computing: Potential barriers play a key position in quantum computing, wherein they control qubits’ conduct, allowing the manipulation of quantum states for advanced computing abilities.
- Transistor Design: In present day transistors, capacity obstacles are critical for controlling the drift of fee companies, providing the foundation for incorporated circuits and microprocessors.
- Scanning Tunneling Microscopes (STM): STMs utilize capability obstacles to probe the floor of materials at the atomic stage, permitting scientists to observe the association of atoms with first-rate precision.
- Memory Devices: In reminiscence gadgets like flash reminiscence, potential obstacles are used to manipulate the float of electrons, permitting records garage and retrieval in diverse client electronics.
- Optoelectronics: Potential boundaries are used in optoelectronic gadgets which include light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and laser diodes, in which they manage electron and hollow recombination, generating mild.
FAQ About Potential Barrier Definition
1. What is a Potential Barrier in Physics?
A potential barrier is a region where a particle encounters an energy threshold that it cannot classically overcome unless its energy is higher than the barrier. In quantum mechanics, particles may still pass through the barrier by tunneling.
2.How Does a Potential Barrier Affect Particles?
The “Potential Barrier Definition” describes how particles are reflected if their energy is lower than the barrier height. However, in quantum mechanics, particles can tunnel through the barrier even with lower energy.
3. What Causes a Potential Barrier?
Potential barriers are caused by changes in the potential energy of a system, such as a change in the electric or magnetic field, which creates a region that a particle finds difficult to pass through.
4 What Is the Role of Potential Barriers in Semiconductors?
In semiconductors, potential barriers control electron flow between different regions, which is essential in the operation of devices like diodes and transistors.






