How does binary fission differ from multiple fission Binary fission and multiple fission are both methods of asexual reproduction observed in certain organisms, but they differ in their processes and outcomes. In binary fission, a single parent organism divides into two equal-sized daughter cells, each containing a complete set of genetic material. This process is commonly seen in bacteria and some single-celled eukaryotes, such as amoebas. Conversely, multiple fission involves the parent organism dividing into multiple daughter cells simultaneously, resulting in the formation of several offspring cells at once. These offspring cells may vary in size and genetic content and are typically smaller than the parent cell. Multiple fission is commonly observed in certain protists, such as some species of Plasmodium, the parasite responsible for malaria. While both binary and multiple fission are methods of asexual reproduction, their distinct processes lead to different outcomes in terms of the number and genetic makeup of the resulting offspring cells.
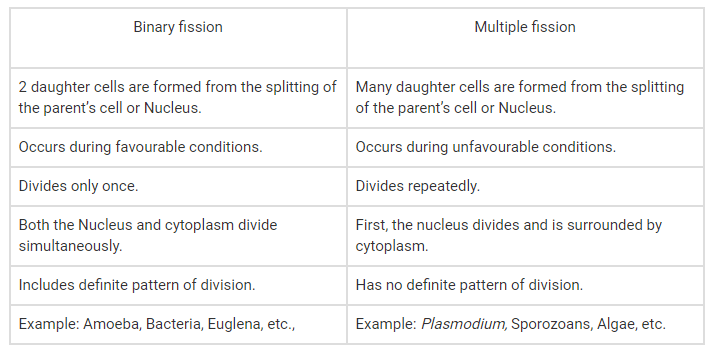
Differences Between Binary Fission and Multiple Fission
How does binary fission differ from multiple fission
- Process:
- Binary Fission: In binary fission, a single parent organism divides into two equal-sized daughter cells, each containing a complete set of genetic material.
- Multiple Fission: In multiple fission, the parent organism divides into multiple daughter cells simultaneously, resulting in the formation of several offspring cells at once.
2. Number of Offspring:
- Binary Fission: Binary fission produces two daughter cells.
- Multiple Fission: Multiple fission produces multiple daughter cells, typically more than two.
3. Genetic Content:
- Binary Fission: Each daughter cell produced by binary fission contains a complete set of genetic material identical to the parent cell.
- Multiple Fission: Daughter cells produced by multiple fission may vary in genetic content and size, as they may contain only a portion of the parent cell’s genetic material.
4. Occurrence:
- Binary Fission: Binary fission is commonly observed in bacteria and some single-celled eukaryotes.
- Multiple Fission: Multiple fission is commonly observed in certain protists, such as some species of Plasmodium, the parasite responsible for malaria.
5. Cellular Division:
- Binary Fission: Binary fission involves the division of a single parent cell into two daughter cells.
- Multiple Fission: Multiple fission involves the division of a single parent cell into multiple daughter cells simultaneously.
Adaptations and Evolutionary Significance
Certainly! Here are the key points outlining adaptations and their evolutionary significance:
- Definition:
- Adaptations are traits or characteristics that enhance the survival and reproductive success of organisms in their environment.
2. Types of Adaptations:
- Adaptations can be physical (e.g., body structures), behavioral (e.g., mating rituals), or physiological (e.g., metabolic processes).
3. Evolutionary Significance:
- Adaptations arise through the process of evolution by natural selection, where individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce.
- Over time, adaptations accumulate within populations, driving the diversification and specialization of species.
4. Role in Survival:
- Adaptations enable organisms to exploit specific niches within their ecosystems, allowing them to compete for resources and avoid predation.
- Examples include camouflage, mimicry, and specialized feeding structures.
5. Role in Reproductive Success:
- Adaptations also play a crucial role in reproductive success by improving an organism’s ability to attract mates, compete for mates, or care for offspring.
- Examples include elaborate courtship displays, bright plumage, and parental care behaviors.
6. Effect on Fitness:
- Traits that confer higher fitness, or reproductive success, are more likely to be passed on to future generations, leading to the proliferation of beneficial adaptations.
- This process drives the adaptation of organisms to their environments over time.
7. Diversification of Life:
- Adaptations contribute to the diversity and complexity of life on Earth, as organisms evolve to occupy different ecological niches and respond to changing environmental conditions.
Applications in Research and Industry
Applications in research and industry harness the principles of adaptation to address various challenges and advance scientific understanding. Here are the key points outlining their significance:
- Biotechnology:
- Adaptations found in organisms, such as extremophiles living in extreme environments, inspire the development of biotechnological solutions.
- Enzymes from extremophiles are used in industrial processes requiring high temperatures or extreme pH conditions.
2. Medicine:
- Understanding the adaptations of disease-causing organisms, like antibiotic resistance in bacteria, guides the development of new treatments and diagnostic tools.
- Research on the adaptive immune system leads to the development of vaccines and immunotherapies.
3. Agriculture:
- Breeding programs utilize adaptive traits in plants and animals to develop varieties with increased yield, disease resistance, or tolerance to environmental stressors.
- Genetic engineering techniques introduce specific adaptations into crops, enhancing their productivity and nutritional value.
4. Environmental Monitoring:
- Monitoring changes in the adaptations of species, such as shifts in migration patterns or phenological events, provides insights into the impacts of climate change and habitat degradation.
- Genetic tools are used to assess the genetic diversity of populations and monitor the spread of invasive species.
5. Bioremediation:
- Microbial adaptations for breaking down pollutants are exploited in bioremediation processes to clean up contaminated environments.
- Engineered microorganisms with enhanced biodegradation capabilities are used to treat soil, water, and air pollution.
6. Materials Science:
- Mimicking adaptations found in nature, such as the self-cleaning properties of lotus leaves or the strength of spider silk, inspires the development of novel materials with unique properties.
- Biomimetic approaches lead to the design of lightweight and durable materials for aerospace, construction, and medical applications.
7. Drug Discovery:
- Exploring the adaptations of organisms in extreme environments, such as deep-sea microbes or desert plants, uncovers bioactive compounds with pharmaceutical potential.
- Screening natural products for their medicinal properties leads to the discovery of new drugs for various diseases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study and application of adaptations play a pivotal role in research and industry, driving innovation, addressing How does binary fission differ from multiple fission challenges, and advancing scientific understanding. By harnessing the principles of adaptation found in nature, scientists and engineers develop solutions that benefit various sectors, from biotechnology and medicine to agriculture and materials science. Adaptations inspire the development of novel biotechnological tools, guide the discovery of new drugs, improve agricultural productivity, and inform environmental monitoring and remediation efforts. Furthermore, insights into adaptations contribute to our understanding of evolution, biodiversity, and the interconnectedness of life on Earth. Overall, the study and application of adaptations continue to enrich our lives, propel technological advancements, and deepen our appreciation for the remarkable diversity of life.
FAQs
Q: 1What is binary fission?
Ans: Binary fission is a form of asexual reproduction where a single parent organism divides into two equal-sized daughter cells.
Q: 2What is multiple fission?
Ans: Multiple fission is a form of asexual reproduction where a single parent organism divides into multiple daughter cells simultaneously.
Q:3 How many offspring does binary fission produce?
Ans: Binary fission produces two daughter cells.
Q: 4 How many offspring does multiple fission produce?
Ans: Multiple fission produces multiple daughter cells, typically more than two.






