Can your family history be traced? Want to know who were your ancestors and were they famous? Where are their origins? If you want the answers to these unsolved puzzles then Genealogist is the concerned person.
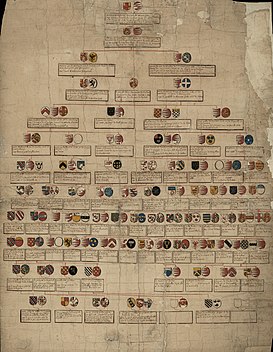
Genealogy is the study of the family history of a person and determining the line of ancestors of a person in the form of diagrams and maps.
Genealogy has seen rapid popularity in recent times due to TV programmes such as ‘Who do you think you are?’ and also due to the availability of family history information on websites like Ancestry and Find my Past.
Genealogists have been working for centuries. For proving their right to lands and titles and to show dynastic links, it had been important to prove one’s line of descent.
The career opportunities in this field have increased due to a great interest in genealogy and family history and technological developments with the availability of online resources.
A Genealogist traces the family histories of clients by using a variety of public and private records such as court records, immigration records and original tax books. For tracing a person’s genealogy, the professional researcher creates charts, maps and reports.
Required Genealogy Skills
- Undergo research operations in libraries, courtrooms and other archives that hold the necessary records of the people you plan to research on.
- Find and be familiar with historical laws of areas of focus.
- Be aware of a wide variety of record types like court records, land records, census records concerned with your locality or area of speciality.
- If required, plan to incorporate DNA into the business, understand chromosomes functionality, shared matches, triangulation and centimorgans.
- Subscribe to a variety of online databases and follow the Genealogical Proof Standard and implement it in your work.
- Become a member of genealogical society at the local, state or national level and religiously attend its meetings. Actively participate in organizing field trips, conducting classes, performing official duties and other activities.
- Increase Genealogy learning by attending local and national conferences, going to genealogical institutes and online genealogy courses.

Required Business Skills
- Should have strong communication skills, time and financial management and organizational skills.
- Develop a realistic business plan that should support you on payment generated.
- Should have an attorney for review of contract language and should maintain standard contract for services.
- Consider the consequences of confidentiality and liability.
- Good oral communication skills and marketing of your services.
- Delivering research reports for the concerned clients.
Entry into genealogy
No formal education is required for a genealogist but knowledge and sufficient experience is required in fields like genealogy, social and local history, palaeography is required. Prior experience in historical research, librarianship, and archive administration can be turned into a professional genealogy career.
The board for certification of Genealogists offers 6 varied certification courses that are:
- Certified Genealogist,
- Certified Genealogical Record Specialist,
- Certified American Lineage Specialist,
- Certified American Indian Lineage Specialist,
- Certified Genealogical Instructor, and
- Certified Genealogical Lecturer.
Various Genealogy job titles
Genealogy professions bring their investigative and tracking skills to work when chasing a client’s ancestors. The different job titles for a genealogist are:
- Private Investigator: These professionals are employed by clients to find about people’s whereabouts for lawsuits, finding an heir or for land properties. The clients can be attorneys who want to secure the minerals and other rights for a living heir and normal public. They need to make an action plan and look up for records like last known locations which can be licensing boards, lawsuits etc.
- Investigative Genetic Genealogist: This professional search for a person’s birth family using DNA testing. DNA profiles from crime scenes are taken and how two people are related is determined using investigative techniques.
- Historic Preservationist: Restoration of cemeteries, a compilation of home and business histories is done by this professional. If you want a building to be named as a historic site, a lineage has to be built in a particular format for a historic preservation office on a state level.
- Military Repatriation Expert: The professional does genealogical research for the military for the location of relatives or kins of servicemen who were part of past wars. After finding about the kin, the next task is the Army’s casualty office can establish contact with them. Testing the relatives’ samples for matching with the remains.
- Heir searcher: His job is to track down all the eligible heirs of an estate and provide the necessary evidence to prove their relationship with the dead person. They are employed by attorneys, courts and estate administrators.
- Citizenship Reclamation Specialist: These experts help people reclaim their ancestral citizenship by needing official documents like birth and school records.

– Chandni Sethia






