The tesla (T) is the magnetic field’s SI unit. It bears Nikola Tesla’s name, an American electrical engineer and inventor of Serbian descent. One coulomb of charge traveling perpendicular to the magnetic field at a speed of one meter per second produces a force of one newton, which is known as a tesla. Due to its size, the tesla is frequently used in combination with smaller units, like the millitesla (mT) or the microtesla (T). Being a vector quantity, the magnetic field has both magnitude and direction. The magnetic field’s direction is denoted by the direction
Introduction
The magnetic field is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude and direction. The direction of the magnetic field is indicated by the direction of the force that it would exert on a moving charge.
SI Unit of Magnetic Field
- The SI unit of H magnetic field is amperes per meter.
- The SI unit of B magnetic field is Newtons per meter per ampere or Teslas.
The SI unit used to measure the magnetic field is tesla (T). Thus, one tesla is that magnetic field in which a charge of one colomb moving with a velocity of 1 m/s perpendicular to the magnetic field experiences a force of one newton
Standard Units
| Parameter | Measuring Unit | Relationship |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | volt (V or E) | E=I×R |
| Current | amp (I) | I=ER |
| Resistance | ohm (R or Ω) | R=EI |
| Conductance | mho (G or ℧℧) | G=IR=IE |
| Power | watt (W) | P=I×Eor P=I2R |
| Inductance | henry (L or H) | VL=−L(ΔIΔt)) |
| Capacitance | farad (C) | C=QE(Q−charge) |
How to Measure Unit of Megnatic Field
There are many ways to measure the unit of magnetic field. Some of the most common methods include:
- Hall effect sensor: A Hall effect sensor is a device that uses the Hall effect to measure the magnetic field. The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference across a conductor when it is placed in a magnetic field.
- Gauss meter: A Gauss meter is a device that measures the magnetic field strength in gauss. Gauss is a unit of magnetic field strength that is equal to 1 tesla.
- Teslameter: A Teslameter is a device that measures the magnetic field strength in tesla. Teslameter is a more sensitive device than a Gauss meter and can be used to measure weaker magnetic fields.
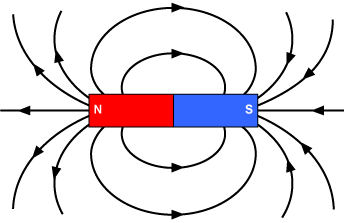
Representation of Magnetic Field
- Field lines are denser at magnetic poles where the magnetic field density is highest.
- Where the magnetic field is weaker and further away, the field lines are less thick.
Magnetic fields are represented by the parallel straight lines with equal intervals. - A small magnetic point’s north-seeking orientation determines the flux’s direction at all times.
- The magnetic fields can be modeled mathematically as a vector field.
- The magnetic fields around here are limitless; they never stop and never intersect.
Magnetic Force
- A point of charge (q) with a specified velocity (v) and time (t) is present at point (r) while being surrounded by an electric field (E) and a magnetic field (B). It is possible to write the magnetic force on electric charge q as:
Related Units
| Unit | Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Tesla (SI unit) | T | One tesla is equal to one weber per square meter. |
| Gauss (CGS unit) | G | One gauss is equal to one maxwell per square centimeter. |
| Oersted (CGS unit) | Oe | One oersted is equal to one ampere per meter. |
| Maxwell (CGS unit) | Mx | One maxwell is equal to one weber per ampere. |
Things to Remember
- Magnetic fields are represented using two symbols H and B in which H denotes magnetic field strength and B denotes magnetic flux.
- The SI unit of magnetic field – H is amperes per meter while the SI unit of B is Teslas or Newtons per meter per ampere.
- Magnetic field lines cannot cross each other. They are endless continuous loops
- In the CGS system, the smallest unit of the magnetic field is Gauss.
- The Relationship between Gauss & Tesla is 1T = 10000G.
- According to Lorentz Force law, q [v X B] is a vector product of Velocity & magnetic field.
- If v & B are parallel or anti-parallel, the vector product of forces becomes zero. Only any moving charge will feel the magnetic force
FAQs
The SI unit of magnetic field is the tesla (T). One tesla is equal to one weber per square meter (Wb/m2).
The tesla was chosen as the SI unit of magnetic field because it is a convenient unit for measuring the strength of magnetic fields. It is also a relatively new unit, which makes it easier to use in calculations.
- Gauss (G): One gauss is equal to one maxwell per square centimeter (Mx/cm2).
- Oersted (Oe): One oersted is equal to one ampere per meter (A/m).
- Maxwell (Mx): One maxwell is equal to one weber per ampere (Wb/A).
1 T = 1000 G
1 T = 10000 Oe
1 T = 1 Wb/A






