Are you brand new to the programming industry? Does “Data Structures and Algorithms” (DSA) make you feel uneasy? Not to worry! In this post, we will deconstruct the DSA’s intricacy into manageable chunks. You’ll have a better idea of what DSA involves and how it serves as the foundation of effective programming at the conclusion of this essay.
Table of Contents
- UTR Full-Form: Introduction to UTR
- UTRFull-Form: Types of UTR
- UTRFull-Form: Functions of Untranslated Regions (UTRs)
- UTR Full-Form: Gene Expression Regulation via UTRs
- UTR Full-Form: Importance of UTRs in Disease
- UTR Full-Form: Experimental Techniques for UTR Analysis
- UTR Full-Form: Experimental Techniques for UTR Analysis
- UTR Full-Form: UTRs in Therapeutic Development
- UTR Full-Form: Evolutionary Conservation and UTRs
- UTR Full-Form: Future Directions in UTR Research
- UTR Full-Form: Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Introduction to UTR
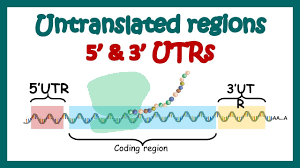
Flanking Regions: UTRs are located at both ends of an mRNA molecule, surrounding the coding sequence. The 5′ UTR, which comes before the coding sequence, and the 3′ UTR, which comes after it, are the two primary forms of UTRs.
Regulatory Functions: UTRs are involved in regulating various aspects of gene expression, including the control of translation efficiency, mRNA stability, and localization. They contribute to the fine-tuning of protein production within the cell.
Translational Control: UTRs in the 5′ region can influence the initiation of translation by interacting with components of the translation machinery. They can contain elements that enhance or repress translation, affecting the rate at which the mRNA is translated into a protein.
Post-Transcriptional Regulation: Elements within UTRs can interact with regulatory molecules such as microRNAs (miRNAs) and RNA-binding proteins (RBPs). These interactions can impact mRNA stability and determine whether the mRNA is targeted for degradation or used for translation.
Alternative Splicing: UTRs can also be influenced by alternative splicing events, where different UTR sequences are included or excluded from the mature mRNA. This process can lead to the production of different protein isoforms from a single gene.
Functional Evolution: UTRs are subject to evolutionary pressures and can accumulate changes over time. Conserved UTR sequences often indicate functional importance in gene regulation.
Disease Implications: Mutations or variations in UTRs can have significant effects on gene expression regulation and contribute to various diseases, including genetic disorders and cancer.
Types of UTR
5′ Untranslated Region (5′ UTR): The 5′ UTR lies upstream of the mRNA’s coding sequence. It contains elements like the 7-methylguanosine cap, essential for translation initiation. Regulatory motifs, such as upstream open reading frames (uORFs), influence protein synthesis. The 5′ UTR guides ribosomal attachment to the mRNA, initiating translation.
3′ Untranslated Region (3′ UTR): The 3′ UTR resides downstream of the coding sequence. It impacts mRNA stability, localization, and translation. MicroRNA binding sites within the 3′ UTR enable post-transcriptional regulation. The 3′ UTR also contains polyadenylation signals, which affect mRNA processing and stability. It plays a vital role in post-transcriptional gene expression control.


Functions of Untranslated Regions (UTRs):
Regulatory Roles: UTRs govern gene expression post-transcriptionally. The 5′ UTR regulates translation initiation by forming ribosomal complexes. It hosts regulatory motifs influencing translation efficiency. The 3′ UTR controls mRNA stability, impacting overall mRNA levels in the cell. It interacts with microRNAs and RNA-binding proteins, directing mRNA fate.
Response to Cellular Signals: UTRs integrate cellular cues, adjusting gene expression in response to environmental changes. They act as platforms for regulatory molecules to exert control, enabling cells to adapt dynamically.
Disease Implications: Dysregulation of UTR-mediated processes contributes to diseases. Mutations in UTR elements can disrupt translation, stability, and localization, leading to pathogenic outcomes. Understanding UTR functions is crucial for unraveling complex regulatory networks and developing targeted therapies.
Protein Localization: UTRs guide mRNA localization within cells. They contain signals that help mRNA reach specific subcellular compartments, ensuring proper protein synthesis in precise locations.
Alternative Splicing Control: UTRs influence alternative splicing, impacting protein isoform diversity. They contain exonic splicing enhancers/silencers that modulate splice site selection.


Gene Expression Regulation via UTRs:
Translational Control: 5′ UTRs influence translation initiation, modulating ribosomal assembly and starting codon recognition. Regulatory motifs affect translation efficiency, allowing cells to fine-tune protein synthesis.
Post-Transcriptional Regulation: 3′ UTRs determine mRNA stability and localization. They interact with microRNAs and RNA-binding proteins, controlling mRNA degradation and translation repression. UTRs collectively orchestrate precise gene expression regulation.


Importance of UTRs in Disease and Research
Importance of UTRs in Disease: UTR mutations disrupt gene regulation, contributing to disorders. Altered translation, stability, and localization lead to abnormal protein expression. Studying UTRs aids disease understanding and potential therapeutic strategies targeting these dysregulated processes.
Importance of UTRs in Research: UTRs unveil intricate gene regulation mechanisms. Unraveling their roles enhances our grasp of cellular processes, aiding drug development and precision medicine. Research on UTRs elucidates post-transcriptional control, RNA-protein interactions, and their relevance in health and disease.
Experimental Techniques for UTR Analysis
- Transcriptomics Approaches: RNA-sequencing unveils transcript profiles, aiding UTR identification. 5′ and 3′ RACE techniques capture UTR ends, essential for annotation accuracy.
- Ribosome Profiling: This maps ribosome positions, revealing translation dynamics across UTRs. It helps understand translational regulation.
- CLIP and RIP Methods: Crosslinking techniques like CLIP and RIP reveal RNA-protein interactions, spotlighting UTR-binding proteins and miRNA interactions.
- Bioinformatics Tools: Algorithms predict UTR motifs, secondary structures, and regulatory elements, aiding functional predictions.
UTRs in Therapeutic Development
- Precision Gene Regulation: UTRs offer targets for therapies modulating translation, stability, and localization. They enable precise control of protein levels, beneficial for gene therapies.
- RNA-Based Therapeutics: Modified UTRs can enhance RNA stability, translation, or miRNA interactions, influencing disease-associated gene expression. UTR engineering aids in developing RNA-based therapies.
- Cancer Treatment: Targeting UTRs disrupts oncogenic pathways. UTR-directed therapies hold promise in halting tumor growth and metastasis.
- Personalized Medicine: UTR analysis tailors therapies, considering individual genetic variation, potentially improving treatment efficacy.
Evolutionary Conservation and UTRs:
- Functional Significance: Conserved UTR regions across species suggest vital roles in gene regulation. Evolutionary pressure preserves critical UTR elements involved in translation, stability, and localization.
- Comparative Genomics: Analyzing UTR sequences in diverse species uncovers conserved motifs. Such motifs may serve essential functions across evolutionary time scales.
- Non-Coding RNA Evolution: Evolutionarily conserved UTRs may host non-coding RNAs with regulatory roles, influencing various cellular processes.
- Phylogenetic Studies: Comparing UTR sequences aids in constructing genealogies, tracing evolutionary relationships among species based on shared regulatory elements.
UTRs in Therapeutic Development
- Precision Gene Regulation: UTRs offer targets for therapies modulating translation, stability, and localization. They enable precise control of protein levels, beneficial for gene therapies.
- RNA-Based Therapeutics: Modified UTRs can enhance RNA stability, translation, or miRNA interactions, influencing disease-associated gene expression. UTR engineering aids in developing RNA-based therapies.
- Cancer Treatment: Targeting UTRs disrupts oncogenic pathways. UTR-directed therapies hold promise in halting tumor growth and metastasis.
- Personalized Medicine: UTR analysis tailors therapies, considering individual genetic variation, potentially improving treatment efficacy.
Future Directions in UTR Research:
- Integrated Systems Biology: UTR studies will merge with broader cellular networks to comprehend gene regulation as a holistic system, enhancing our understanding of complex biological processes.
- Single-Cell Analysis: Investigating UTRs at single-cell resolution will unveil cell-specific regulatory patterns, providing insights into cellular diversity and responses.
- Functional Validation: Advances in genome editing and synthetic biology will enable precise manipulation of UTRs, allowing researchers to validate their functional roles and therapeutic potential.
- Therapeutic Innovations: UTR-targeted therapies, enabled by deeper insights, will contribute to precision medicine approaches, addressing genetic diseases and disorders with greater accuracy.
UTR - Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Untranslated Regions (UTRs) are segments flanking the coding sequence of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. They don’t directly code for proteins but play essential roles in gene regulation and post-transcriptional processes.
The 5′ UTR is the sequence upstream of the coding region, involved in translation initiation and ribosome binding. The 3′ UTR is downstream, influencing mRNA stability, localization, and interactions with regulatory molecules like microRNAs.
UTRs impact gene expression by influencing translation efficiency, mRNA stability, and localization. They contain regulatory elements that interact with proteins and RNA molecules, modulating the fate of the mRNA.
Mutations or dysregulation of UTRs can disrupt gene expression, leading to diseases. Altered UTR functions can result in abnormal protein levels, affecting cellular processes and contributing to disorders.
Techniques like RNA-sequencing, ribosome profiling, and crosslinking methods (CLIP, RIP) provide insights into UTR functions. Bioinformatics tools predict UTR motifs and regulatory elements, aiding functional analysis.
Conserved UTR regions across species suggest important regulatory roles. Analyzing UTR sequences in different species helps identify essential functional elements that have been preserved over evolutionary time.
UTRs can integrate cellular signals and environmental cues, allowing cells to adjust gene expression levels in response to changes in their environment or developmental stages. This contributes to cellular adaptation and regulation.
Yes, UTRs can contain exonic splicing enhancers or silencers that impact alternative splicing, leading to the production of different protein isoforms from the same gene.






