ETL processes are fundamental in data warehousing and are used to integrate data from different sources into a single. ETL processes are fundamental in business intelligence, enabling organizations to make informed decisions by providing clean, transformed, and accessible data for analysis and reporting purposes..
- ETL Full Form: Extract, Transform, Load
- ETL Full Form: Efficient Transfer of Loads
- ETL Full Form: Enhanced Text Localization
- ETL Full Form: Environmental Testing Laboratory
- ETL Full Form: Education Through Leadership
- ETL Full Form: The Role of ETL in Modern Data Integration
- ETL Full Form: How ETL Simplifies Data Management and Analysis
- ETL Full Form: Emergency Telecommunications Link
- ETL Full Form: Energy Transition Lab
- ETL Full Form: Engineering Technology Laboratory
- ETL Full Form: Entertainment Technology and Lighting
- ETL: Evaluation, Testing, and Learning
- The Future of ETL: Trends and Innovations in Data Integration
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
ETL Full Form: Extract, Transform, Load
Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) is a crucial process in data integration and warehousing. It involves gathering data from various sources, manipulating it to fit operational needs, and loading it into a destination where it can be analyzed and utilized effectively. Here’s a breakdown of the ETL process:
- Data Extraction: ETL begins by extracting data from diverse sources such as databases, files, APIs, and more.
- Source Connectivity: ETL tools establish connections to source systems, enabling the extraction of raw data.
- Raw Data Collection: Raw data, in its unprocessed form, is gathered and prepared for transformation.
- Data Cleansing: Raw data often contains inconsistencies and errors. ETL processes clean and sanitize the data, ensuring accuracy.
- Data Transformation: Various operations like sorting, filtering, aggregating, and enriching are applied to the cleansed data. This step ensures data consistency and relevancy.
- Business Rules Application: ETL tools apply predefined business rules to transform the data into a format suitable for analysis and reporting.
Load:
- Destination Setup: ETL tools configure the destination database or data warehouse where transformed data will be stored.
- Data Loading: The transformed and processed data is loaded into the destination, making it available for querying and analysis.
- Data Indexing: In databases, indexes may be created to optimize query performance, enabling faster access to the loaded data.
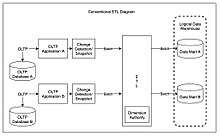


ETL Full Form: Efficient Transfer of Loads
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Load Assessment | – Evaluate the nature and weight of the load.<br>- Determine suitable equipment for the specific load. |
| Safety Precautions | – Implement safety measures for workers and surroundings.<br>- Use appropriate safety gear and protocols. |
| Load Preparation | – Secure the load properly for transport.<br>- Use strapping, wrapping, or containers as necessary. |
| Efficient Transfer | – Utilize efficient equipment and machinery for load transfer.<br>- Minimize handling to save time and effort. |
| Optimal Routing | – Plan the route considering load size, weight, and road conditions.<br>- Opt for the shortest and safest path. |
| Constant Monitoring | – Continuously monitor the load during transfer.<br>- Address any issues promptly to prevent accidents. |
| Unload Safely | – Unload the load with care and precision.<br>- Use appropriate tools and equipment for unloading. |
| Post-Transfer Inspection | – Inspect the load, equipment, and surroundings after transfer.<br>- Address any damages or issues immediately. |
ETL Full Form: Enhanced Text Localization
Enhanced Text Localization (ETL) is a specialized process in the field of translation and content adaptation. It involves the meticulous adaptation of textual content to make it culturally relevant, linguistically accurate, and contextually appropriate for specific target audiences. ETL is particularly significant in global marketing, software localization, and international communication, ensuring that messages resonate effectively with diverse cultures and languages. Below are the key components of the Enhanced Text Localization process presented in a detailed manner:
- In-depth research on the target culture’s norms, traditions, and sensitivities.
- Adaptation of content to align with cultural preferences, ensuring it resonates with the local audience.
Linguistic Precision:
- Translation by native speakers with a deep understanding of both source and target languages.
- Focus on linguistic nuances, idiomatic expressions, and colloquialisms to maintain natural language flow.
- Localization of images, symbols, and colors to suit cultural significance and avoid misinterpretation.
- Adapting content contextually, considering regional differences in humor, references, and metaphors.
Technical Integration:
- Integration of localized text into software interfaces, websites, or multimedia content.
- Ensuring proper display, readability, and functionality of localized text within the intended platforms.
- Rigorous testing to verify linguistic accuracy, cultural appropriateness, and technical functionality.
- Iterative feedback and revisions to enhance the localized content based on user experience and feedback.
ETL Full Form: Environmental Testing Laboratory
| Function | Activities |
|---|---|
| Sample Collection | – Gather samples of air, water, soil, and other materials from specific environmental sources.<br>- Follow standardized protocols to ensure sample integrity. |
| Sample Preparation | – Process samples to remove impurities and prepare them for analysis.<br>- Utilize various techniques like filtration and extraction. |
| Instrumental Analysis | – Employ advanced instruments such as spectrometers, chromatographs, and sensors to analyze samples quantitatively and qualitatively.<br>- Detect pollutants and contaminants accurately. |
| Chemical and Biological Tests | – Conduct chemical tests to identify and quantify substances present in the samples.<br>- Perform biological tests to assess the impact of pollutants on living organisms. |
| Data Interpretation | – Analyze and interpret test results, comparing them to regulatory standards and guidelines.<br>- Generate detailed reports outlining findings and recommendations. |
| Quality Control | – Implement strict quality control measures to ensure the accuracy and reliability of test results.<br>- Regularly calibrate instruments and validate methodologies. |
| Environmental Monitoring | – Monitor environmental changes over time by conducting regular sampling and analysis.<br>- Provide valuable data for environmental impact assessments and trend analysis. |
ETL Full Form: Education Through Leadership
Education Through Leadership (ETL) is an innovative approach to learning that emphasizes the development of leadership skills and qualities among students. This educational philosophy goes beyond traditional classroom teaching, focusing on empowering individuals with the skills and mindset necessary to lead and make a positive impact in various fields. The ETL methodology incorporates several key principles and practices, fostering holistic growth and preparing students for future leadership roles. Here are the core components of Education Through Leadership, presented in bullet-point format:
- Structured leadership training programs that teach communication, decision-making, and problem-solving skills.
- Practical exercises and simulations to apply leadership concepts in real-world scenarios.
Mentorship and Guidance:
- Mentorship programs connect students with experienced leaders and professionals.
- Personalized guidance and coaching to help students identify their strengths and areas for growth.
- Encouragement to participate in community service projects and initiatives.
- Collaboration with local organizations and NGOs to address social issues, promoting a sense of responsibility and civic engagement.
Interdisciplinary Learning:
- Integration of leadership concepts into various academic disciplines, encouraging interdisciplinary thinking and problem-solving.
- Emphasis on creativity, innovation, and adaptability to prepare students for diverse leadership challenges.
Ethical Leadership Development:
- Focus on ethics, integrity, and social responsibility in leadership practices.
- Discussions and workshops on moral dilemmas, ethical decision-making, and responsible leadership in a global context.
ETL Full Form: The Role of ETL in Modern Data Integration
1. Introduction to ETL in Data Integration
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) performs a critical function in current statistics integration through facilitating the motion of statistics throughout a couple of structures. It guarantees statistics from diverse reassets is blended right into a single, on hand repository for analysis. ETL techniques assist companies make statistics-pushed selections successfully.
2. Extract: Gathering Data from Multiple Sources
The extraction section includes gathering uncooked statistics from a couple of heterogeneous reassets like databases, APIs, and flat files. ETL structures have to manage each dependent and unstructured statistics to make sure all applicable facts is captured. Proper extraction guarantees the statistics is prepared for transformation.
3. Transform: Converting Data for Consistency and Usability
Transformation guarantees the extracted statistics is cleaned, formatted, and dependent in step with commercial enterprise requirements. This manner consists of statistics cleansing, normalization, aggregation, or even validation. It`s essential for standardizing statistics from various reassets for steady use.
4. Load: Ingesting Data into the Target System
The loading section includes shifting the converted statistics right into a goal system, along with a statistics warehouse or database. This step calls for optimization to make sure the statistics is loaded successfully and may be accessed through customers or programs with out delay.
5. ETL`s Role in Data Warehousing
ETL is a cornerstone in statistics warehousing because it consolidates statistics from specific reassets right into a imperative repository. This integration makes it less complicated for agencies to investigate huge volumes of statistics throughout departments. It helps commercial enterprise intelligence (BI) and decision-making techniques.
6. Improving Data Quality Through ETL
One of the important thing roles of ETL is enhancing the fine of statistics through disposing of duplicates, correcting errors, and managing lacking values. Ensuring first rate statistics complements the accuracy of analytics, main to higher decision-making and insights.
7. ETL in Real-Time Data Integration
While conventional ETL techniques had been batch-primarily based totally, current structures can manner statistics in real-time. Real-time ETL permits companies to reply fast to converting commercial enterprise conditions, offering up to date insights and enhancing operational efficiency.
8. ETL vs. ELT: Choosing the Right Approach for Data Integration
While ETL has been the conventional method, the more recent ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) method is gaining recognition in cloud-primarily based totally environments. ELT shifts the transformation to after the statistics is loaded into the goal system, providing scalability and quicker processing for huge datasets.
ETL Full Form: How ETL Simplifies Data Management and Analysis
1. Centralizes Data Collection
ETL extracts records from more than one reassets and centralizes it right into a unified database or warehouse. This removes the want to look throughout diverse structures for records.
2. Streamlines Data Transformation
ETL transforms uncooked records right into a regular layout that may be without difficulty analyzed. This step consists of cleaning, filtering, and changing records right into a established shape appropriate for evaluation.
3. Improves Data Accuracy
By standardizing and validating records all through the transformation manner, ETL reduces errors, inconsistencies, and duplicates, making sure fantastic records for decision-making.
4. Enhances Data Accessibility
Once transformed, records is loaded right into a centralized garage machine, making it without difficulty on hand for evaluation and reporting. This simplifies the records retrieval manner for users.
5. Automates Data Workflows
ETL automates the manner of extracting, transforming, and loading records, decreasing the want for guide interventions and saving time in records control tasks.
6. Optimizes Performance
With ETL, massive datasets are processed efficiently, making sure that records is to be had for evaluation with out compromising machine performance. This permits quicker decision-making.
7. Supports Real-Time Data Processing
ETL may be configured for real-time records processing, making sure that organizations usually have get right of entry to to the maximum up to date statistics for well timed insights.
8. Facilitates Advanced Analytics
By organizing and cleaning records, ETL makes it less complicated to use superior analytics and device studying algorithms, imparting deeper insights for strategic decision-making.
ETL Full Form: Emergency Telecommunications Link
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Redundant Communication Channels | – Establish multiple communication channels (satellite, radio, cellular) to ensure connectivity even if one network fails.<br>- Redundancy guarantees continuous communication in the event of network outages. |
| Emergency Broadcast Systems | – Implement systems for broadcasting emergency alerts and warnings to the public.<br>- Utilize sirens, text messages, and social media to disseminate critical information swiftly. |
| Priority Communication Services | – Provide priority access to emergency responders, government officials, and humanitarian organizations during crises.<br>- Ensure these entities can communicate without network congestion delays. |
| Data Transmission and GIS | – Enable data transmission capabilities for sharing maps, disaster assessments, and resource deployment plans.<br>- Utilize Geographical Information Systems (GIS) for mapping affected areas and planning response efforts effectively. |
| Interagency Collaboration Tools | – Implement collaborative platforms for different agencies and organizations involved in disaster response.<br>- Enable real-time information sharing and coordination among multiple stakeholders. |
| Community Engagement Platforms | – Utilize social media and web platforms to engage with the public and gather real-time information on the situation.<br>- Encourage community participation and provide updates on evacuation routes and emergency services. |
| Power Backup and Resilience | – Install backup power systems (generators, solar panels) to ensure continuous operation during power outages.<br>- Enhance resilience against natural disasters by reinforcing infrastructure and protecting communication facilities. |
ETL Full Form: Energy Transition Lab
Energy Transition Lab (ETL) refers to a specialized facility or initiative focused on researching, testing, and promoting sustainable energy solutions. These labs serve as crucial hubs for innovation, aiming to accelerate the shift from traditional fossil fuel-based energy systems to renewable and environmentally friendly alternatives. ETLs play a pivotal role in shaping the future of energy production, distribution, and consumption. Here are the key aspects of an Energy Transition Lab presented in bullet-point format:
- Conduct in-depth research on renewable energy technologies, energy storage systems, and energy efficiency measures.
- Explore innovative methods for harnessing solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and other renewable sources.
Testing and Prototyping:
- Develop prototypes and test new energy technologies for reliability, efficiency, and scalability.
- Evaluate the performance of renewable energy systems under various conditions and optimize their designs.
- Collaborate with policymakers, industry stakeholders, and communities to advocate for supportive energy transition policies.
- Provide data-driven recommendations to influence energy policies and regulations, fostering a conducive environment for renewable energy adoption.
Community Engagement:
- Raise awareness about sustainable energy practices through educational programs, workshops, and outreach activities.
- Engage with local communities to promote energy conservation, renewable energy adoption, and sustainable living practices.
- Forge partnerships with universities, research institutions, businesses, and government agencies for collaborative research and development initiatives.
- Facilitate knowledge exchange and collaborative projects to accelerate the deployment of sustainable energy solutions.
ETL Full Form: Engineering Technology Laboratory
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Advanced Equipment | – Housing specialized machinery and instruments for precision engineering tasks.<br>- Includes CNC machines, 3D printers, and materials testing devices. |
| Prototyping Facilities | – Providing resources for creating prototypes of engineering designs and products.<br>- Allows engineers to test concepts and refine designs iteratively. |
| Simulation Tools | – Utilizing computer-based simulations for modeling and analyzing engineering systems.<br>- Enables virtual testing and optimization of complex structures. |
| Electronics Testing | – Conducting experiments and tests on electronic components and circuits.<br>- Includes oscilloscopes, signal generators, and circuit simulation software. |
| Materials Analysis | – Analyzing the properties and behaviors of materials, including tensile strength, hardness, and thermal conductivity.<br>- Essential for material selection in engineering projects. |
| Environmental Testing | – Evaluating the impact of environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and vibration on engineering products.<br>- Ensures products’ reliability under various conditions. |
| Collaborative Spaces | – Designated areas for collaboration, brainstorming, and team-based engineering projects.<br>- Promotes interdisciplinary teamwork and knowledge exchange. |
| Safety Protocols | – Implementing strict safety measures to ensure the well-being of lab personnel and maintain a secure working environment.<br>- Training staff on safety protocols and emergency procedures. |
ETL Full Form: Entertainment Technology and Lighting
Entertainment Technology and Lighting (ETL) is a multifaceted field that combines technical expertise with creativity to enhance various forms of entertainment, including theater productions, concerts, theme parks, and live events. ETL professionals work with advanced technologies to create immersive experiences, ensuring optimal lighting, sound, and visual effects. Here’s a breakdown of the key components and functions within Entertainment Technology and Lighting, presented in bullet-point format:
- Conceptualize and design lighting setups to create specific moods and atmospheres.
- Utilize computer software for simulations and precise control of lighting elements.
Sound Engineering:
- Design and implement audio systems for clear and immersive sound experiences.
- Balance sound levels, optimize acoustics, and integrate speakers and amplifiers.
- Integrate visual effects technologies such as projections, LED screens, and holograms into live performances.
- Sync visual effects with lighting and sound for seamless and captivating presentations.
Automation and Control:
- Implement automation systems to control lighting changes, sound cues, and special effects.
- Use control consoles and software for real-time adjustments during performances.
- Ensure the safe installation and operation of equipment, including rigging lights and sound systems.
- Adhere to industry standards and safety protocols to prevent accidents during setup and performances.
Collaboration and Coordination:
- Collaborate with directors, producers, set designers, and performers to align technical aspects with creative visions.
- Coordinate with stagehands and technicians for efficient setup, rehearsals, and dismantling of equipment.
ETL Full Form: Evaluation, Testing, and Learning
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Evaluation | – Assessing the effectiveness and efficiency of existing processes, programs, or products.<br>- Identifying strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement through data analysis and feedback. |
| Testing | – Conducting controlled experiments, simulations, or assessments to validate hypotheses or test new methods and innovations.<br>- Collecting empirical data to measure outcomes and performance. |
| Learning and Adaptation | – Analyzing evaluation and testing results to extract valuable insights and lessons learned.<br>- Applying knowledge to refine strategies, enhance processes, and implement improvements. |
| Iterative Approach | – Embracing an iterative cycle of evaluation, testing, and learning to continually refine and optimize processes or products.<br>- Implementing feedback loops for continuous improvement. |
| Data-Driven Decision Making | – Utilizing data and analytics to make informed decisions based on evaluation and testing outcomes.<br>- Applying evidence-based practices to drive strategic and operational decisions. |
| Stakeholder Engagement | – Involving relevant stakeholders in the evaluation and testing process to gather diverse perspectives and insights.<br>- Encouraging collaboration and knowledge sharing among stakeholders. |
| Knowledge Dissemination | – Sharing insights, best practices, and lessons learned with stakeholders and the wider community.<br>- Promoting a culture of learning and knowledge exchange within the organization or community. |
The Future of ETL: Trends and Innovations in Data Integration
1. Cloud-Based ETL Solutions
Cloud systems are revolutionizing information integration via way of means of imparting scalable and cost-powerful ETL answers. Cloud-primarily based totally equipment permit for higher flexibility, faraway get right of entry to, and integration with numerous cloud-local information services. The shift to the cloud is making ETL techniques greater green and collaborative.
2. Real-Time ETL Processing
As agencies call for greater well timed insights, real-time ETL is turning into a key trend. Instead of batch processing, information is processed and converted as it’s far ingested, permitting quicker decision-making. This shift enables agencies live in advance in unexpectedly converting environments.
3. AI and Machine Learning in ETL
AI and system gaining knowledge of technology are being incorporated into ETL equipment to automate and beautify information extraction and transformation techniques. These technology can expect information anomalies, optimize workflows, and enhance the accuracy of transformations. ML-pushed ETL is enhancing performance and lowering guide errors.
4. Data Virtualization
Data virtualization is a method that lets in customers to get right of entry to information with out bodily shifting it. Instead of conventional ETL techniques, information virtualization permits real-time get right of entry to to dispensed information sources. This reduces complexity and improves flexibility in information integration.
5. Automation and Orchestration of ETL Pipelines
Automation equipment are more and more more getting used to streamline ETL workflows, lowering guide intervention and growing the reliability of information techniques. Orchestration systems permit seamless coordination of various ETL tasks, ensuing in quicker information glide and advanced productivity.
6. Integration of Big Data with ETL
With the upward push of large information, ETL techniques are evolving to deal with massive volumes, variety, and speed of information. Big information technology like Hadoop and Spark are being integrated into ETL pipelines to control large datasets greater efficiently. This enables agencies benefit insights from numerous and unstructured information sources.
7. Self-Service ETL Tools
Self-carrier ETL equipment permit enterprise customers to control and create their personal information pipelines with minimum IT involvement. These user-pleasant systems democratize information get right of entry to and empower non-technical groups to carry out information integration tasks. It promotes agility and faster decision-making throughout departments.
8. Data Governance and Security in ETL
As information privateness worries grow, ETL techniques are incorporating more potent safety and governance measures. Ensuring information quality, lineage, and compliance with policies like GDPR is critical. Future ETL answers will emphasize encryption, steady get right of entry to, and auditability to protect information integrity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Yes, IG in Chat is accessible on both Android and iOS devices, ensuring widespread availability.
Absolutely! Many businesses and influencers utilize IG in Chat for customer engagement and brand promotion.
Yes, IG in Chat employs end-to-end encryption and robust privacy settings to safeguard user conversations.
Currently, IG in Chat supports text-based communication, but the platform might introduce video call features in the future.
You can download IG in Chat from the respective app stores on your device. Simply search for “Instagram” and install the app to access IG in Chat features.
ETL ensures that data is accurate, consistent, and accessible, allowing for meaningful analysis and decision-making. It helps organizations consolidate data from different systems into a single repository.
Some popular ETL tools include Apache Nifi, Talend, Informatica PowerCenter, Microsoft SSIS (SQL Server Integration Services), and Apache Airflow.






