ESG full form is “Environmental, Social, and Governance“. It refers to a set of criteria that investors and organizations use to evaluate a company’s performance and impact in these key areas In this article we will tell you about “ESG Full Form: Benefits, Challenges, Future and more”.
Overview
In the tapestry of responsible corporate practices, Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations emerge as threads of ethical and sustainable conduct. ESG encapsulates a trifecta of principles that guide organizations in nurturing environmental consciousness, fostering social responsibility, and upholding governance integrity. This holistic framework intertwines financial success with ethical stewardship, amplifying a company’s societal impact. By championing ESG, businesses traverse a path towards resilience, transparency, and alignment with global sustainability objectives, epitomizing the fusion of profit and purpose.
Know further about this article “ESG Full Form: Benefits, Challenges, Future and more” below.
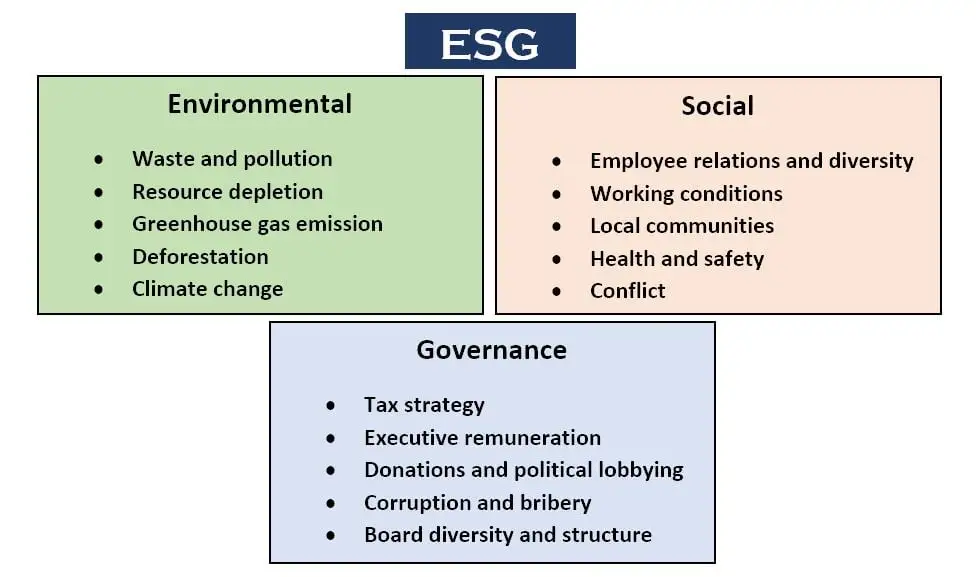


Environmental Factors
1. Climate Action: In an era of climate consciousness, corporations navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by climate change. Mitigation strategies, carbon footprint reduction, and renewable energy adoption emerge as instrumental components.
2. Resource Management: Efficient utilization of finite resources lies at the core of environmental considerations. From water conservation to waste reduction, prudent resource management minimizes ecological strain.
3. Biodiversity Preservation: The safeguarding of biodiversity and natural habitats underscores the responsibility of businesses. Ecosystem protection and sustainable sourcing practices harmonize economic growth with ecological balance.
4. Pollution Mitigation: Mitigating pollution emissions and minimizing ecological harm is paramount. Strategies encompass emissions control, sustainable waste disposal, and curbing hazardous material usage.
5. Energy Efficiency: Championing energy efficiency manifests as a linchpin in corporate environmental efforts. Embracing innovative technologies and practices reduces energy consumption, thus curbing carbon emissions.
6. Circular Economy: Transitioning towards a circular economy model fosters resource regeneration and waste reduction. Companies reimagine production and consumption cycles, embodying sustainability.
7. Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the labyrinth of environmental regulations is pivotal. Organizations adhere to legal mandates while aspiring to exceed compliance, enhancing ecological stewardship.
8. Sustainable Supply Chains: Environmental considerations extend along supply chains. Organizations embrace suppliers aligned with sustainable practices, thus amplifying their eco-friendly footprint.
Social Considerations
1. Diversity and Inclusion: A commitment to diversity and inclusion catalyzes a culture of equity and acceptance. Organizations value diverse perspectives, fostering an inclusive environment that reflects the mosaic of society.
2. Labor Standards: Upholding fair labor practices is paramount. Ethical treatment of employees, equitable wages, and safe working conditions epitomize social responsibility.
3. Human Rights: A staunch dedication to human rights aligns with ethical conduct. Companies ensure their operations respect human rights principles and contribute positively to communities.
4. Community Engagement: Active community engagement enriches corporate impact. Organizations collaborate with local communities, bolstering social well-being through initiatives and partnerships.
5. Philanthropy and CSR: Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and philanthropy underscore commitment beyond profits. Contributing to social causes, education, healthcare, and societal development embodies responsible citizenship.
6. Stakeholder Communication: Transparent and open communication with stakeholders forms a bedrock. Addressing concerns, sharing progress, and involving stakeholders foster trust and alignment.
7. Ethical Sourcing: Sourcing practices uphold ethical standards. Companies ensure suppliers adhere to ethical labor and production practices, steering clear of exploitative processes.
8. Consumer Welfare: Prioritizing consumer well-being extends beyond products. Ethical marketing, quality assurance, and data privacy resonate with social considerations.
Governance Practices
1. Board Independence: A cornerstone of governance, an independent board ensures unbiased decision-making. Directors devoid of conflicts of interest uphold the sanctity of corporate oversight.
2. Transparency and Accountability: Transparency in operations and financial reporting fosters trust. Accountability ensures that decisions are justly made and their outcomes are upheld.
3. Shareholder Rights: Respecting shareholders’ rights, including voting and access to information, underscores governance. Equitable treatment ensures stakeholders’ voices are heard.
4. Ethical Conduct: Ethical codes permeate corporate culture. Upholding honesty, integrity, and ethical behavior among employees and leadership sets a governance foundation.
5. Risk Management: Effective risk management aligns with governance. Identifying and mitigating risks ensures that potential pitfalls are addressed proactively.
6. Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to legal mandates showcases governance prowess. Meeting regulatory requirements while upholding ethical standards ensures organizational legitimacy.
7. Executive Compensation: Transparent and fair executive compensation practices reflect prudent governance. Aligning executive pay with performance fosters accountability.
8. Conflict of Interest Mitigation: Mitigating conflicts of interest among leadership and employees safeguards governance. A robust framework prevents undue influences.
Know further about this article “ESG Full Form: Benefits, Challenges, Future and more” below.
Benefits of ESG Integration
- Enhanced Sustainability: ESG integration cultivates a foundation of sustainable practices, enabling organizations to thrive while minimizing negative impacts on the environment and society.
- Improved Reputation: Organizations championing ESG principles bolster their reputation, becoming beacons of responsible conduct that resonate with consumers, investors, and stakeholders.
- Attraction of Capital: ESG-conscious enterprises appeal to investors seeking ethically aligned opportunities, potentially accessing a broader pool of capital and fostering financial stability.
- Risk Management: ESG integration hones risk management practices, enabling companies to identify and mitigate potential risks, safeguarding long-term operational stability.
- Innovation Catalyst: ESG principles spur innovation, inspiring organizations to create sustainable products, services, and processes that meet evolving societal needs.
- Employee Engagement: ESG initiatives resonate with employees, fostering a sense of purpose and engagement as they contribute to causes aligned with their values.
- Competitive Advantage: ESG integration provides a competitive edge by differentiating organizations as leaders in sustainability, attracting conscious consumers and partners.
Know further about this article “ESG Full Form: Benefits, Challenges, Future and more” below.
Challenges of ESG
- Data Quality and Availability: Accurate ESG reporting relies on robust data collection. The challenge lies in sourcing reliable data across complex supply chains and disparate systems.
- Measurement and Metrics Standardization: The lack of standardized metrics and benchmarks makes it challenging to compare ESG performance across industries, hindering accurate assessment.
- Balancing Short-Term and Long-Term Goals: ESG initiatives often require long-term investments that may conflict with short-term financial targets, posing challenges for financial decision-makers.
- Integration Complexity: Effectively integrating ESG principles into existing business operations demands careful consideration of diverse factors, from technology to culture.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging stakeholders effectively to align their expectations with ESG goals is complex, as interests can vary among investors, employees, customers, and communities.
- Regulatory Variability: ESG regulations and reporting requirements vary across jurisdictions, presenting challenges in navigating a patchwork of compliance standards.
- Greenwashing Risks: Misrepresentation of ESG efforts, or “greenwashing,” threatens trust and credibility. Ensuring genuine alignment of practices and communication is paramount.
FAQs about ESG
Companies can integrate ESG principles by aligning their business strategies with environmental sustainability, promoting social responsibility, and implementing transparent and ethical governance practices. This involves setting measurable goals, reporting on progress, and engaging stakeholders.
Investors can assess ESG performance by analyzing ESG reports, metrics, and ratings. These can include carbon emissions data, diversity statistics, employee engagement initiatives, board composition, and ethical governance practices.
ESG is evolving from a trend to a fundamental business strategy. It aligns with societal expectations, regulatory shifts, and investor preferences for responsible practices. Companies integrating ESG are better positioned for long-term success.






