IoT full form is “Internet of Things.” It is a concept that refers to the network of physical objects or “things” embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that enable them to connect and exchange data over the internet. These connected objects can range from everyday devices like smartphones, smartwatches, and home appliances to more specialized industrial machines and infrastructure.
- Core Concepts of IoT
- IoT Applications : IOT full form
- History : IOT full form
- Differences Between IoT and IIoT: IOT full form
- Components : IOT full form
- Types of Sensors: IOT full form
- Working: IOT full form
- Advantages : IOT full form
- Disadvantages: IOT full form
- Characteristics: IOT full form
- Security Challenges : IOT full form
- Privacy Challenges in IoT
- IOT Data Analytics and Machine Learning
- Future Trends in IoT
- Challenges in IoT
- FAQs about IoT
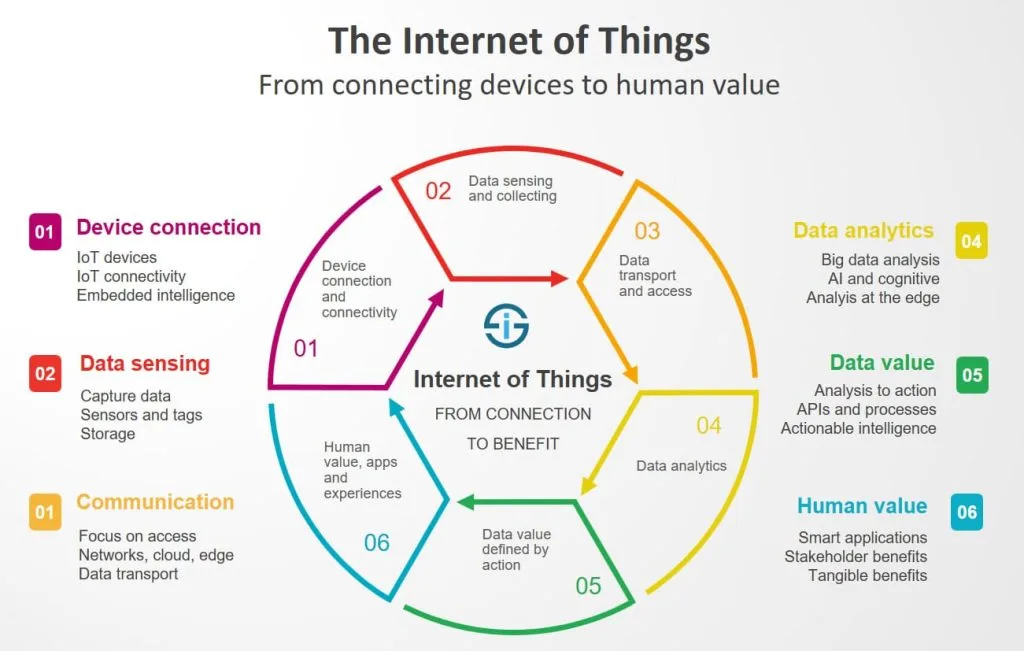


Core Concepts of IoT
- Connected Devices/Things: IoT revolves around physical objects or devices, often referred to as “things,” that are embedded with sensors, actuators, and connectivity capabilities. These devices can range from everyday objects like smartphones and wearables to industrial machines, smart home appliances, and environmental sensors.
- Sensors and Actuators: IoT devices are equipped with sensors to detect changes in their environment and gather data. Actuators enable devices to perform actions based on the data received. For example, a temperature sensor in a smart thermostat can collect data, and the actuator can adjust the temperature accordingly.
- Connectivity: IoT devices use various communication technologies to connect to the internet and transmit data. Common connectivity options include Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, RFID, cellular networks, and LPWAN technologies.
- Data Collection and Transmission: IoT devices continuously collect data from their environment through sensors. They then transmit this data to cloud-based platforms or edge computing systems for further processing and analysis.
- Internet/Cloud Connectivity: IoT devices communicate with cloud-based platforms to store and process data. Cloud connectivity allows for centralized data storage, real-time processing, and access to remote services.
IoT Applications and Use Cases
Some prominent IoT applications and use cases:
- Smart Home Automation: IoT enables the automation and remote control of various devices in a home, such as smart thermostats, lighting systems, security cameras, door locks, and appliances. Users can manage and monitor these devices using smartphones or voice-activated assistants.
- Healthcare and Remote Patient Monitoring: IoT devices are used in healthcare for remote patient monitoring, wearable health trackers, smart medical devices, and telemedicine applications. These technologies enable real-time health data collection and provide personalized health insights.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT) and Industry 4.0: IIoT uses IoT technology to optimize industrial processes, improve efficiency, and enable predictive maintenance in manufacturing, logistics, supply chain management, and other industries.
- Smart Agriculture: IoT applications in agriculture include soil monitoring, automated irrigation systems, livestock monitoring, crop health monitoring, and precision agriculture, leading to improved productivity and sustainability.
- Smart Cities: IoT is used in smart city initiatives for traffic management, waste management, environmental monitoring, energy efficiency, public safety, and better urban planning.
- Connected Vehicles and Transportation: IoT enables connected vehicles with features like vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication, vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication, and telematics. It improves road safety, traffic management, and enhances the driving experience.
- Environmental Monitoring: IoT-based environmental sensors are deployed to monitor air quality, water quality, weather conditions, and pollution levels. This data helps in environmental conservation and disaster management.
History : IOT full form
Early Concepts (1982): The concept of IoT began in the early 1980s when a Coca-Cola vending machine at Carnegie Mellon University was modified to report its inventory and whether newly loaded drinks were cold.
Term Coined (1999): The term “Internet of Things” was coined by Kevin Ashton, a British technologist, during his work at Procter & Gamble to describe a system where the internet is connected to the physical world via sensors.
Adoption of RFID (2000s): The use of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology expanded IoT capabilities, allowing objects to be tracked and monitored, marking a significant advancement in IoT development.
Smart Devices Introduction (2007-2010): The rise of smartphones and smart home devices (like smart thermostats and lights) integrated IoT technology into everyday life, making IoT more mainstream.
IPv6 Adoption (2011): The introduction of IPv6 provided a virtually unlimited number of IP addresses, which is essential for the scalability of IoT, as it allows more devices to be connected to the internet.
Rapid Growth (2010s): IoT saw explosive growth in the 2010s, with applications in various sectors like healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation. The number of IoT devices surpassed the world’s population in 2017.
Standardization and Security Focus (2020s): With the massive growth of IoT, efforts increased to standardize protocols and improve security measures to protect data and privacy as IoT became more integrated into critical infrastructure and daily life.
Differences Between IoT and IIoT: IOT full form
| Aspect | IoT (Internet of Things) | IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Consumer-oriented applications | Industrial and manufacturing applications |
| Common Applications | Smart homes, wearable devices, health monitoring, etc. | Industrial automation, predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, etc. |
| Data Usage | Personal and lifestyle data | Operational and production data |
| Scale of Deployment | Typically smaller scale, such as homes and individual devices | Large-scale deployments in factories, plants, and industrial sites |
| Security Concerns | Focus on data privacy and secure communication | Emphasis on system integrity, safety, and preventing operational disruptions |
| Network Reliability | Often relies on consumer-grade networks (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth) | Requires highly reliable, industrial-grade networks (Ethernet, 5G, etc.) |
| Standards and Protocols | Uses standards like Wi-Fi, Zigbee, MQTT | Uses industrial protocols like Modbus, OPC-UA, and industrial Ethernet |
Components : IOT full form
Sensors and Actuators: These gadgets gather information from the surroundings (e.G., temperature, humidity) and perform moves based at the facts (e.G., turning on a mild).
Connectivity Modules: These include communique technology including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and cellular networks that allow devices to transmit records to different gadgets or networks.
Edge Devices: Devices that procedure facts regionally earlier than sending it to the cloud, decreasing latency and bandwidth utilization (e.G., smart thermostats, protection cameras).
Cloud Computing Platforms: Services and infrastructure that keep, analyze, and control records collected from IoT devices, presenting scalability and remote get entry to.
Data Analytics Tools: Software and algorithms that examine facts to generate insights, discover patterns, and make predictions based totally at the collected facts.
User Interfaces: Applications or dashboards that allow customers to have interaction with IoT gadgets, screen records, and manage settings (e.G., mobile apps, net portals).
Security and Privacy Mechanisms: Protocols and technologies that shield IoT systems from unauthorized get admission to, facts breaches, and make certain user privateness (e.G., encryption, authentication).
Types of Sensors: IOT full form
| Sensor Type | Description | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Sensor | Measures temperature changes. | Weather stations, smart thermostats, HVAC systems. |
| Humidity Sensor | Measures moisture levels in the air. | Weather monitoring, agriculture, climate control. |
| Proximity Sensor | Detects the presence or absence of objects or their distance from the sensor. | Parking sensors, touchless controls, object detection. |
| Pressure Sensor | Measures the force exerted by a fluid or gas. | Weather forecasting, industrial processes, automotive systems. |
| Accelerometer | Measures acceleration forces, detecting changes in velocity. | Mobile phones, fitness trackers, vehicle dynamics. |
| Gyroscope | Measures rotational movement around an axis. | Navigation systems, drones, gaming controllers. |
| Light Sensor | Measures light intensity or ambient light levels. | Automatic lighting systems, photography, environmental monitoring. |
| Gas Sensor | Detects the presence of specific gases in the environment. | Air quality monitoring, industrial safety, home gas leak detection. |
| Motion Sensor | Detects movement or changes in position. | Security systems, smart lighting, energy management. |
| Sound Sensor | Measures sound levels or vibrations. | Noise monitoring, voice-activated devices, environmental noise assessments. |
Working: IOT full form
Sensing: Sensors discover bodily phenomena (e.G., temperature, light, motion) through their unique sensing factors, which convert the detected modifications into an electrical signal.
Signal Conversion: The analog indicators produced with the aid of the sensor are often converted into digital alerts the use of an Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC). This step makes the information suitable for processing by way of digital structures.
Data Transmission: The digital records is then transmitted from the sensor to a microcontroller or gateway thru wired (e.G., UART, SPI) or wireless communique protocols (e.G., Wi-Fi, Bluetooth).
Data Processing: The microcontroller or part device approaches the received information, making use of any important algorithms or calculations to extract significant facts or cause movements based totally on predefined conditions.
Data Transmission to Cloud: Processed records is despatched to a cloud-primarily based server or information platform, where it is able to be similarly analyzed, stored, and controlled. This transmission regularly makes use of protocols together with HTTP, MQTT, or CoAP.
Data Analysis: In the cloud, advanced analytics and gadget getting to know algorithms can be applied to discover patterns, tendencies, or anomalies in the records, presenting insights or predictions primarily based on ancient statistics.
Action and Feedback: Based at the analyzed facts, moves may be taken routinely or thru user commands, along with adjusting a thermostat placing or triggering an alert. Feedback also can be sent back to the person or device for tracking and control functions.
Advantages : IOT full form
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Real-Time Monitoring | Sensors provide continuous, real-time data collection, enabling immediate insights and timely responses. |
| Improved Efficiency | Automation and precise data from sensors lead to optimized processes, reducing waste and increasing productivity. |
| Cost Savings | Early detection of issues and efficient resource management can lead to significant cost reductions over time. |
| Enhanced Decision Making | Data-driven insights from sensors support informed decision-making and strategic planning. |
| Increased Safety | Sensors can monitor hazardous conditions and trigger alerts, enhancing safety in industrial and residential environments. |
| Remote Management | IoT sensors enable remote monitoring and control of devices and systems from anywhere, improving convenience and management. |
| Predictive Maintenance | Sensors help predict equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. |
Disadvantages: IOT full form
| Disadvantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High Initial Costs | The cost of purchasing and installing sensors, along with the infrastructure needed for data transmission, can be high. |
| Data Privacy Concerns | The collection and transmission of sensitive data can raise privacy issues and increase the risk of data breaches. |
| Complexity of Integration | Integrating various sensors into existing systems and ensuring compatibility can be complex and challenging. |
| Maintenance and Reliability | Sensors require regular maintenance and can be prone to malfunctions or inaccuracies, affecting system reliability. |
| Data Overload | The large volume of data generated by multiple sensors can overwhelm data storage and processing systems if not managed properly. |
| Security Risks | Sensors and their communication networks can be vulnerable to cyber-attacks, requiring robust security measures. |
| Limited Battery Life | Many sensors rely on batteries, which can have limited lifespan and require frequent replacement or recharging. |
Characteristics: IOT full form
Sensitivity: The potential of a sensor to locate small changes or low levels of the measured variable. Higher sensitivity way greater unique and accurate measurements.
Accuracy: The degree to which a sensor’s measurements replicate the proper cost of the parameter being measured. Accurate sensors make certain reliable records for analysis and choice-making.
Response Time: The pace at which a sensor responds to adjustments inside the measured parameter. A quick response time is essential for programs requiring actual-time monitoring and short modifications.
Range: The span of values that a sensor can correctly degree. Sensors have to have the right range for their unique software to make sure they seize applicable information.
Resolution: The smallest trade in the measured parameter that a sensor can distinguish. Higher decision lets in for greater detailed and granular facts collection.
Durability: The sensor’s capacity to face up to environmental conditions inclusive of temperature extremes, humidity, vibration, and physical strain. Durable sensors are critical for reliable operation in harsh environments.
Power Consumption: The amount of electricity a sensor requires to operate. Low power intake is essential for battery-powered sensors and for extending the general lifespan of IoT gadgets.
Security Challenges in IoT
- Device Vulnerabilities: IoT devices may have limited computing resources, making them susceptible to security vulnerabilities and attacks.
- Data Breaches: IoT devices collect and transmit sensitive data, and a breach can result in significant privacy violations and data exposure.
- Interoperability Issues: Heterogeneity in devices and communication protocols can create interoperability challenges, leading to security gaps.
- Inadequate Authentication and Authorization: Weak or missing authentication mechanisms can allow unauthorized access to IoT devices and data.
- Lack of Encryption: Data transmitted between devices and cloud platforms may be susceptible to interception if not adequately encrypted.
- Firmware and Software Updates: IoT devices may not receive regular updates, leaving them vulnerable to known exploits.
- Physical Security: Physical access to IoT devices can compromise their security, especially in industrial or critical infrastructure settings.
- DDoS Attacks: IoT devices can be compromised to launch Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
Privacy Challenges in IoT
- Data Collection and Profiling: IoT devices continuously collect data, raising concerns about user privacy and the potential for data profiling.
- Data Storage and Retention: The storage of sensitive data on cloud platforms must adhere to strict privacy regulations to prevent unauthorized access.
- User Consent and Transparency: Users may not always be fully aware of the data collected by IoT devices, leading to privacy concerns.
- Third-Party Access: Sharing data with third-party services and applications can raise privacy issues if not adequately controlled.
- Data Ownership: Determining data ownership and rights in IoT ecosystems can be complex, affecting user privacy.
- Data Anonymization: Ensuring data is properly anonymized and aggregated to protect individual identities is crucial for privacy.
IoT Data Analytics and Machine Learning
The combination of IoT Data Analytics and Machine Learning allows organizations to make more informed decisions, automate processes, and optimize operations. By applying ML algorithms to IoT data, organizations can gain valuable predictive and prescriptive insights, leading to increased efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced user experiences. It enables the creation of smart and autonomous systems that continuously learn and adapt based on real-world data, bringing the vision of a truly intelligent IoT ecosystem closer to reality.
Future Trends in IoT
- 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks will significantly impact IoT by offering faster data transfer rates, lower latency, and increased network capacity. This will enable more real-time applications and support a higher number of connected devices.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, reducing the need for centralized cloud processing. This trend will lead to faster response times, reduced data transfer, and improved privacy and security.
- AI and ML Integration: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) will play a crucial role in IoT by enabling smarter and more autonomous devices. ML algorithms will analyze IoT data to provide valuable insights and predictions.
- Blockchain Integration: Blockchain technology will enhance IoT security and enable trusted and decentralized communication among IoT devices, reducing the risk of data tampering.
- IoT in Smart Cities: IoT will drive the development of smart cities, with interconnected systems for traffic management, waste management, energy efficiency, and public safety.
- IoT in Healthcare: IoT will revolutionize healthcare with remote patient monitoring, wearable health devices, and improved medical diagnosis and treatment.
- IoT in Agriculture: Smart agriculture will be enhanced by IoT applications like precision farming, automated irrigation, and livestock monitoring.
Challenges in IoT
- Security and Privacy: IoT devices are susceptible to security breaches, leading to data theft and privacy violations. Ensuring robust security measures and privacy controls will be a major challenge.
- Interoperability: The diversity of IoT devices and communication protocols can hinder seamless interoperability, requiring standardized approaches and frameworks.
- Data Management: Handling the massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices poses challenges in terms of storage, processing, and analytics.
- Power Consumption: Many IoT devices are battery-powered, and optimizing power consumption is crucial to extend device lifetimes and reduce maintenance.
- Scalability: As the number of connected devices grows, IoT systems must be scalable to handle the increasing data traffic and device management.
- Regulatory Compliance: IoT systems must comply with data protection and privacy regulations, which can vary globally.
- Cost and ROI: The initial investment in IoT infrastructure and devices may be substantial, and businesses need to assess the long-term ROI.
FAQs about IoT
Q1:What is an IoT sensor?
A: IoT sensor is a device that detects and measures physical properties (such as temperature, humidity, or motion) and converts this data into a digital format for transmission over a network.
Q2:How do IoT sensors work?
A: IoT sensors detect environmental changes, convert the measurements into digital data, transmit this data to a processing unit or cloud server, and enable real-time monitoring and control.
Q3: What types of data can IoT sensors collect?
A: IoT sensors can collect various types of data, including temperature, humidity, light levels, motion, pressure, gas concentrations, and sound levels.
Q4: What are the benefits of using IoT sensors?
A: Benefits include real-time monitoring, improved efficiency, cost savings, enhanced safety, remote management, and predictive maintenance.
Q5: How are IoT sensors powered?
A: IoT sensors can be powered by various sources, including batteries, external power supplies, or energy harvesting methods (such as solar power).






