A Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA Full-Form), commonly known as a stroke, is a sudden interruption in the brain’s blood supply. This disruption can occur due to a blocked or ruptured blood vessel, leading to a lack of oxygen and nutrients to brain cells. CVAs often result in various neurological impairments, such as paralysis, speech difficulties, or loss of cognitive functions.
Understanding CVA: Cerebrovascular Accident Explained
A Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA), commonly referred to as a stroke, is a serious medical condition that occurs when there is a sudden disruption in the blood flow to the brain. This interruption deprives the brain of essential oxygen and nutrients, leading to damage of brain cells and potential long-term disabilities. Understanding CVA is crucial for early recognition, immediate medical intervention, and prevention. Here’s a breakdown of key points related to CVA:
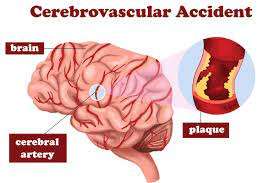
- Types of CVA : There are two main types of strokes – ischemic stroke, caused by a blood clot blocking an artery in the brain, and hemorrhagic stroke, caused by a ruptured blood vessel in the brain.
- Symptoms: Common signs of CVA include sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, confusion, trouble speaking or understanding speech, sudden trouble seeing, walking, dizziness, and severe headache.
- Risk Factors: Several factors increase the risk of stroke, including high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, obesity, and a family history of stroke.
- Prevention: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing blood pressure, quitting smoking, maintaining a balanced diet, and regular exercise can significantly reduce the risk of CVA Full-Form.
- Treatment: Immediate medical attention is crucial. Treatment options include clot-busting drugs, surgical procedures, and rehabilitation therapies to regain lost skills and improve quality of life.


CVA Unveiled: What You Need to Know
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | CVA Full-Form is a sudden interruption in the brain’s blood supply, leading to brain cell damage due to lack of oxygen. |
| Types | – Ischemic Stroke: Caused by a blood clot blocking an artery. – Hemorrhagic Stroke: Due to a ruptured blood vessel in the brain. |
| Symptoms | – Sudden numbness or weakness. – Confusion, trouble speaking, or understanding. – Severe headache. |
| Risk Factors | – High blood pressure. – Diabetes. – Smoking. – Obesity. – Family history of stroke. |
| Prevention | – Maintain a healthy diet. – Regular exercise. – Manage blood pressure. – Quit smoking. |
| Treatment | – Immediate medical attention is crucial. – Clot-busting drugs. – Surgical procedures. – Rehabilitation therapies. |
CVA: A Closer Look at Cerebrovascular Accidents
Cerebrovascular Accidents (CVA Full-Form), commonly known as strokes, are abrupt disruptions in the brain’s blood supply, leading to brain cell damage due to oxygen deprivation.
- Types: CVA Full-Form occur in two main forms: Ischemic Stroke, caused by a blood clot obstructing an artery, and Hemorrhagic Stroke, resulting from a ruptured blood vessel in the brain.
- Symptoms: Recognizable signs include sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, confusion, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, vision problems, dizziness, and severe headache.
- Risk Factors: Certain factors escalate the risk, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, obesity, high cholesterol, and a family history of stroke.
- Prevention: Lifestyle modifications like maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, managing stress, and quitting smoking significantly reduce the risk of CVAs.
- Treatment: Immediate medical attention is crucial. Treatment options include thrombolytic drugs to dissolve clots, surgical interventions, and rehabilitation therapies to regain lost skills and independence.
Decoding CVA: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Causes | – Ischemic Stroke: Caused by a blood clot blocking a brain artery. <br> – Hemorrhagic Stroke: Due to a ruptured blood vessel in the brain. |
| Symptoms | – Sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg. <br> – Confusion, trouble speaking, or understanding. <br> – Severe headache. |
| Risk Factors | – High blood pressure. <br> – Smoking. <br> – Diabetes. <br> – Obesity. <br> – High cholesterol. <br> – Family history of stroke. |
| Prevention | – Adopt a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. <br> – Regular exercise. <br> – Manage stress. <br> – Control blood pressure and cholesterol. <br> – Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. |
| Treatment | – Ischemic Stroke: Thrombolytic drugs to dissolve clots. <br> – Hemorrhagic Stroke: Surgery or endovascular procedures. <br> – Rehabilitation therapies for recovery. <br> – Medications to prevent future strokes. |
The Impact of Cerebrovascular Accidents (CVAs) on Brain Health
Cerebrovascular Accidents (CVAs), or strokes, have significant repercussions on brain health, affecting various aspects of cognitive and physical functioning. Understanding these impacts is crucial for patients and caregivers.
- Brain Damage: CVAs cause immediate brain cell damage due to oxygen deprivation, leading to loss of function in affected areas.
- Cognitive Impairment: Strokes can impair memory, reasoning, and judgment, affecting a person’s ability to make decisions and solve problems.
- Communication Challenges: CVAs often lead to difficulty speaking or understanding language, making communication arduous.
- Motor Skills Impairment: Weakness or paralysis in limbs is common, making mobility and coordination challenging.
- Emotional Changes: Strokes can lead to mood swings, depression, or emotional lability, impacting overall emotional well-being.
- Long-term Disabilities: Depending on the severity, CVAs can result in long-term disabilities, requiring extensive rehabilitation and support.
- Risk of Recurrence: Individuals who have suffered a stroke are at a higher risk of experiencing another, emphasizing the importance of preventive measures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A CVA, commonly known as a stroke, occurs when there is a sudden disruption in the brain’s blood supply, leading to brain cell damage due to lack of oxygen. Strokes can be ischemic (caused by a clot) or hemorrhagic (caused by a ruptured blood vessel).
ommon symptoms include sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg; confusion; trouble speaking or understanding speech; sudden trouble seeing; dizziness; and severe headache.
CVAs are often caused by conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, obesity, and heart diseases, which can damage blood vessels and lead to strokes. Unhealthy lifestyle choices and genetic factors also play a role.
Immediate medical attention is crucial. Treatment includes clot-busting drugs (for ischemic strokes), surgical procedures, and rehabilitation therapies to regain lost skills. Medications are often prescribed to prevent future strokes.
Yes, many strokes are preventable. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing blood pressure, quitting smoking, maintaining a balanced diet, and regular exercise significantly reduce the risk of CVAs.






